Snowpack Summary for Friday, March 2, 2018 6:49 PM 45" (114 cm) of snowfall for February!
This summary expired Mar. 04, 2018 6:49 PM
Flagstaff, Arizona - Backcountry of The San Francisco Peaks and Kachina Peaks Wilderness
Thin coverage and rock/log hits are likely.
Natural avalanches are unlikely, but human triggered avalanches are possible, with increasing likelihood of moderate severity with added weight from wind transport and or precipitation. The weak basal facet structure of the snowpack has shown low strength and moderate to high propagation reactivity.
Currently, year to date snowfall is at 75" (190 cm) at 10,800', with a settled base depth of about 37" (94 cm) on a sheltered NW aspect. 9,500' base depth is @ 22" (56 cm).
Avalanches may be possible near and above treeline where wind slabs have developed with continued wind transport from the south (S) and southwest (SW), as well as strong north (N) winds 2-25-18, though some starting zones are more rocks than snow, especially on south aspects. Observations from the past week in the Inner Basin indicated continued wind slab deposits on a variety of aspects along ridge lines, as well as cross loading at lower elevations, increasing load on existing weak layers.
Basal faceting has been observed on generally N facing aspects near treeline, from ground level up to 30 cm (See snow pit diagrams under the 'Snowpack' tab), and has demonstrated failure and propagation on these facets, though spatially variable.
View snow pits at snowpilot.org.
With similar conditions continuing, a greater likelihood of human triggered wind slabs exists, either in thin starting zones or cross loaded areas below ridge lines.
Watch out for small isolated slabs of new snow, wind deposits and storm accumulation perched on older layers.
Also, the snow depth is highly variable due to wind transport and sun affect, aspect dependent.
Current Problems (noninclusive) more info

With a forecast of possible new snow accumulation accompanied by moderate to strong winds, wind slab creation may increase potential hazard.

Images
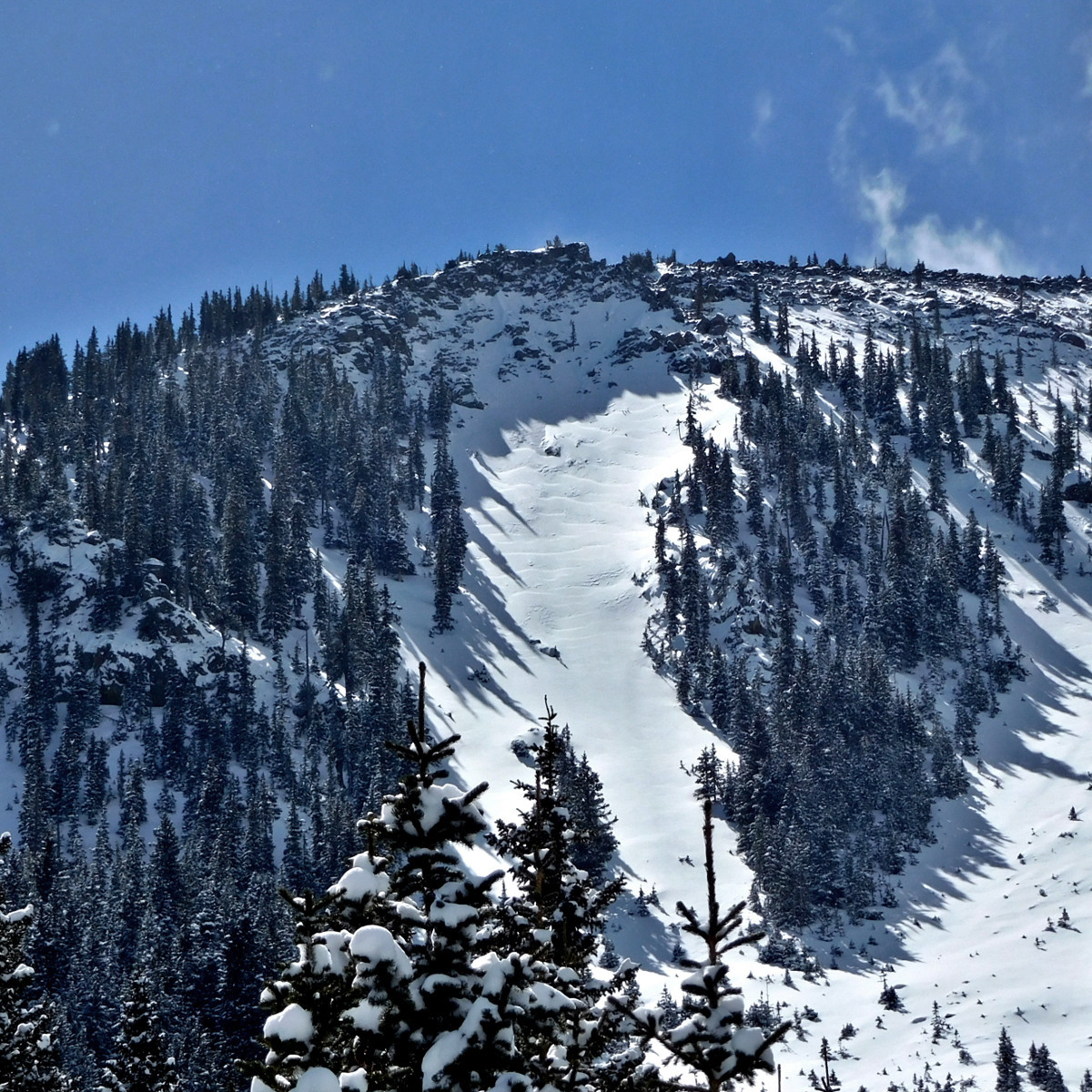

Wind slabs and wind loading at the top of Jay's Slide avalanche path, just below treeline on the northerly slopes of Fremont Peak. February 28, 2018.
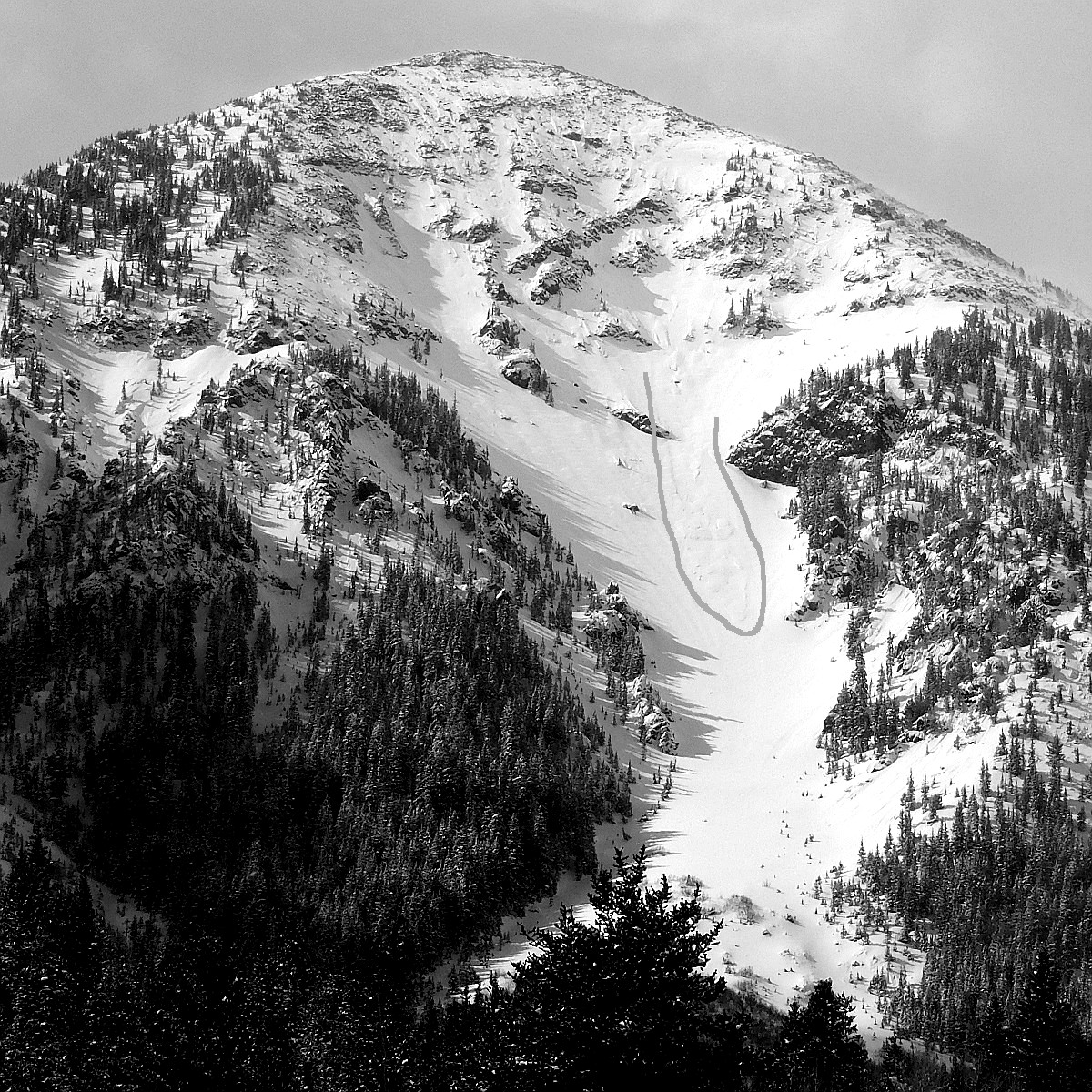

Small storm-snow sluff in Telemark avalanche path, northerly slopes of Fremont Peak. Occurred during the early morning hours of the February 28th storm. Image traced to show sluff.
Final Thoughts
"Uphill travel on terrain within the Arizona Snowbowl ski area is currently unavailable due to mountain operations and construction projects."
https://www.snowbowl.ski/the-mountain/uphill-access/
Weather
Northern Arizona continues to occupy a favorable position within the western storm track, however a bit south of the core energy. Last weekend’s storm produced almost a foot of cold low density snow at treeline. On Tuesday night and Wednesday February 28th another foot plus was laid down at 10,800’. This storm also produced low density cold dendrites (stellar crystals) and was easily moved by moderate storm winds and stronger and gusty winds shifting to north and northwest as the storm passed. Above treeline snow stripping, sublimation, and some slab deposition is evident.
On the horizon, set to enter our region on Saturday night March 3th, one more storm, however this time most of the fireworks appear to be to our north and we are expecting strong winds but little snow accumulation. A warming trend and gusty winds will characterize the upcoming work week.
On Thursday evening, March 1st the Inner Basin SNOTEL site (Snowslide) reported a snow depth of 26 inches (66 cm) at 9730’, and Arizona Snowbowl reported a settled base of 41 inches (104 cm) at 10800'. So far this winter, 75 inches (190.5 cm) of snow has fallen at the mid-mountain study site. Since February 23rd, SNOTEL temperatures ranged between 3° and 40° F. For the same period the AZ Snowbowl Top Patrol Station (ASTP) temperatures ranged between –0.5° and 2 9° F.
Agassiz Peak Station 11500'
Snowslide Canyon Snotel (Inner Basin) 9730′
Authored/Edited By: Troy Marino, Derik Spice